PY - Basic Syntax
安裝 Python
通常執行安裝 Python 時會自動連pip (python 的軟體包管理系統) 一同裝好
- 執行安裝檔,勾選
Add Python 3.11 to PATH,這樣可以直接把 Python 設定為環境變數。 - 打開 cmd,輸入
python --version和pip --version觀察是否成功安裝 Python 和 pip。
Windows 用戶不建議用 Git bash,畫面會卡住
- 同樣在 cmd ,輸入
python,沒意外的話會出現 Python 的執行環境。
在 VScode 中寫 Python
- 安裝 Python 插件來讓 VScode 可以寫 Python。
可以額外安裝 Pylance 提高使用體驗,但一定得先裝 Python
- 在設定中搜尋
code-runner run in terminal,將選項打勾,這樣 Python 的input語法才可以在 VScode 中使用。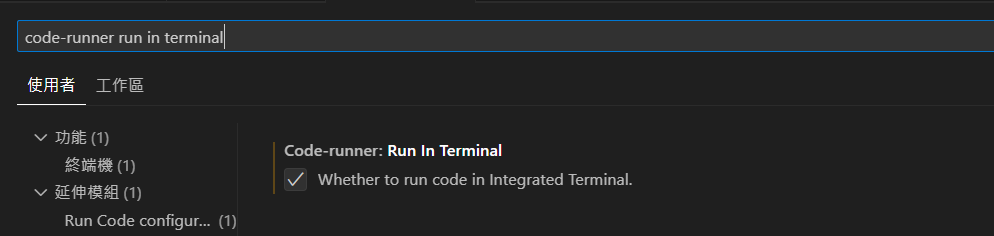
input 允許使用者輸入一段內容,默認型態是字串
Python 基礎語法
在 Python 中,是使用縮排來定義區塊程式碼,以 if-else 舉例:
if A:
# do something
else:
# do another thing
判別式
依據使用者成績輸入來回傳成績等第為範例:
grade = input('enter your grade:')
grade = float(grade)
if grade > 1 or grade < 0:
print('you must enter the number between 0-1')
elif grade >= 0.9:
print('A')
elif grade >= 0.8:
print('B')
elif grade >= 0.7:
print('C')
elif grade >= 0.6:
print('D')
else:
print('F')
函式
以 def 定義函式:
def computepay(a, b):
ta = float(a)
tb = float(b)
if ta < 40:
return ta * tb
else:
return 40 * tb + (ta - 40) * tb * 1.5
hrs = input('enter hours:')
rate = input('enter rate:')
print(computepay(hrs, rate))
函式中的 *args 跟 **kwargs
先來看看下面這一段程式碼:
def numSum(a, b):
return a + b
# answer is 3
print(numSum(1, 2))
# TypeError: numSum() takes 2 positional arguments but 3 were given
print(numSum(1, 2, 3))
可以看到當我們傳入超出函式定義的參數數量時,python 開始報錯,避免這個情況以使我們的函式更具泛用性,我們可以使用 *args 將所有的位置參數捆綁為一個元組傳入:
def numSum(*args):
sum = 0
for i in args:
sum += i
return sum
# answer is 6
print(numSum(1, 2, 3))
更有趣的是,還有個 **kwargs 可以來讓我們將所有的關鍵字參數捆綁為一個字典傳入:
def numSum(**kwargs):
sum=0
for key, value in kwargs.items():
sum+=value
return sum
# answer is 6
print(numSum(apple=1, banana=2, orange=3))
迴圈
While
適用在不知道循環次數,只想針對某一個條件一直執行程式碼時:
while True:
try:
num = input('enter number')
if num == "done":
break
else:
trNum = float(num)
if largest == None and smallest == None:
largest = trNum
smallest = trNum
elif largest < trNum:
largest = trNum
elif smallest > trNum:
smallest = trNum
except:
print('Invalid input')
continue
print('Maximum', largest)
print('Minium', smallest)
上述的意思是,當使用者輸入 done 時,就透過 break 跳出迴圈繼續執行之後的 code,而如果輸入的是數字就一直執行這個迴圈,直到使用者輸入 done 為止。
for
適合用在規定尋換次數下執行程式碼。
for i in range(1, 6):
print(i)
error handling
在 while 迴圈的範例中,有使用 try-except 的用法,這是 Python 中做例外處理的語法,是為了避免程式碼出錯而程式運行中斷而產生的語法。
當上述的範例不使用 try-except:
largest = None
smallest = None
while True:
num = input('enter number')
if num == "done":
break
else:
# 這裡可能會報錯
trNum = float(num)
if largest == None and smallest == None:
largest = trNum
smallest = trNum
elif largest < trNum:
largest = trNum
elif smallest > trNum:
smallest = trNum
print('Maximum', largest)
print('Minium', smallest)
程式碼仍然可以執行,但如果用戶今天輸入的內容無法轉為數字,比如輸入 ABC,因為 float 無法將其轉為浮點數,所以 Python 會噴出一段錯誤 ValueError: could not convert string to float: 'ABC',並中斷程式執行。
靠著 try-except,程式碼會優先執行 try 區塊中的邏輯,當如果出現錯誤才去執行 except 中的事情。
一開始的 while 迴圈中的 try-except 就是跟 Python 說:如果出現錯誤 (使用者輸入無法轉成浮點數的內容),就印出一段訊息,並透過 continue 重新執行迴圈。
針對特定錯誤類型做控制
Python 提供很多特定的錯誤類型提供針對某些特定錯誤做處理。那哪些是特定錯誤,部分列舉如下:
ZeroDivisionErrorSyntaxErrorTypeErrorFileNotFoundError
以下為 Meta b2e 課程範例:
def divide_by(a, b):
try:
return a / b
except ZeroDivisionError:
return 0
except Exception as e:
print(e, 'Something went wrong!')
ans = divide_by(10,0)
print(ans)